

A depressed skull fracture is a break in or crushing of part of the skull.
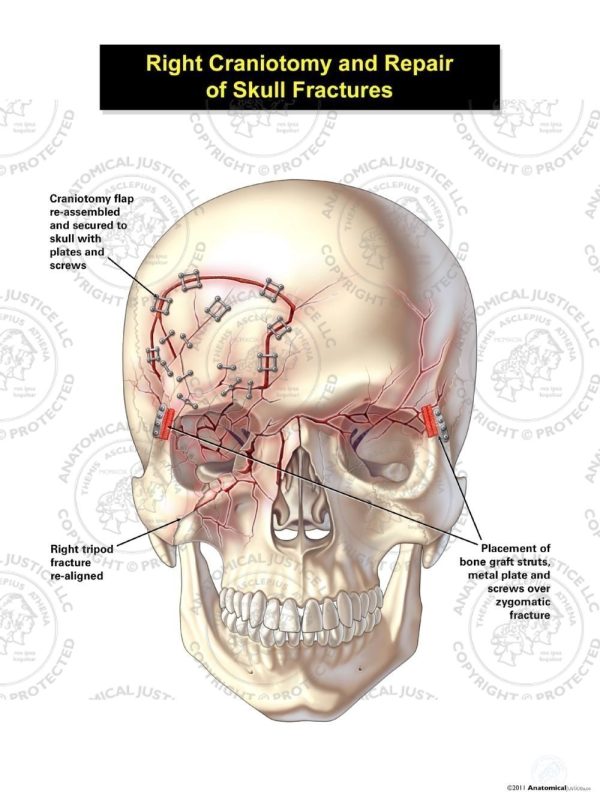
These unjuries are usually moitored and not treated sugically. A linear skull fracture is a break in the skull resembling a thin line or crack.Skull fractures are a concern because a disruption in the skill can cause injury to the brain or provide an open avenue for infection or both. Intraventricular Hemorrhage: Bleeding into the ventricles of the brain.Intracerebral Hematoma: Bleeding within the brain tissue itself caused by the rupture of a blood vessel within the brain.Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Bleeding withing the layers of the dura, specifically under the aracnoid layer.Subdural Hematoma: A blood clot between the brain and the dura.Epidural Hematoma: A blood clot outside of the brain and the dura but under the skull.Intracranial hematomas are the rupture of a blood vessel leading to the collection of blood in brain tissues or empty spaces. Primary injuries include the injuries that are sustained at the time of the traumatic event, such as: Intracranial Hemotomas The more severe the initial insult, the more likely the secondary injuries will have a major effects on the person's overall outcome Primary Injury Most brain injuries are compised of a mix of both primary and secondary injuries. In this, as well as similar injuries to older children, the blood vessels tear causing internal hemorrhaging in addition to the direct damage to the brain tissue. When a baby is shaken, the brain often has several types of injuries including coup contra coup, rotation injuries and swelling. Rotation injuries also result in shearing and tearing of brain tissue.
Other possible types of damage include contusions or bruises that result in swelling. This type of injury may become diffuse because of the shearing and tearing that can occur as the brain moves back and forth within the skull. In contrast, a person whose head hits the pavement after a fall may injure both the area of the brain at the point of impact and the opposite side of the brain as well. A person with this type of injury may have less overall damage as a result, depending on where the injury occurs and the cognitive processes involved in the damaged area of the brain. In addition to the severity of a brain injury, the type of injury can make a difference in a person’s recovery.įor instance, focal and penetrating injuries tend to injure specific portions of the brain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
